Application of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose in Exterior Wall Insulation Systems
Exterior wall insulation is a vital component in enhancing building energy efficiency and reducing heat loss. One material that has gained significant attention for its application in these systems is hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). In this article, we will explore the various uses and advantages of HPMC in exterior wall insulation systems.
Thermal Insulation Properties:
HPMC exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties, making it an ideal choice for exterior wall insulation. Its low thermal conductivity helps to minimize heat transfer through the walls, thereby improving energy efficiency in buildings. By using HPMC as part of the insulation system, the overall U-value of the wall can be significantly reduced, leading to energy savings and improved indoor comfort.
Adhesive and Binding Agent:
HPMC serves as an effective adhesive and binding agent in exterior wall insulation systems. It can be used as a key component in mortar formulations, helping to enhance the adhesion between the insulation materials and the wall surface. The high viscosity of HPMC ensures good workability and easy application, allowing for uniform distribution and optimal bonding strength.
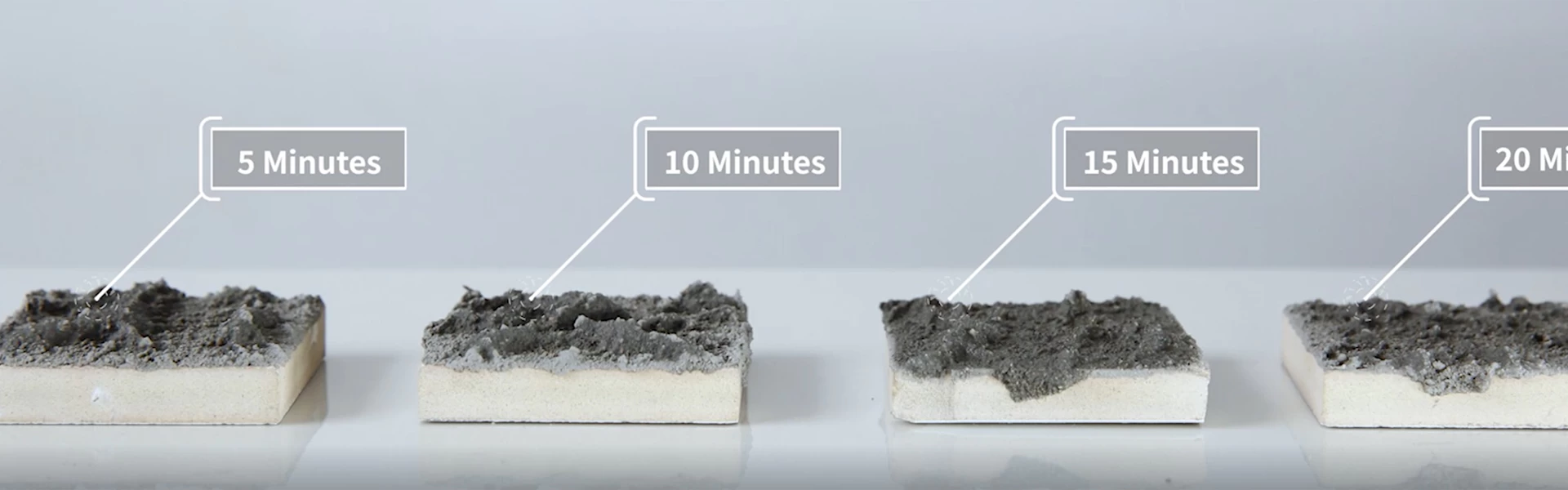
Crack Resistance and Water Retention:
One of the critical challenges faced in exterior wall insulation systems is crack formation due to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and building movements. HPMC plays a crucial role in preventing cracks by improving the flexibility and elasticity of the mortar. It acts as a water retention agent, keeping the mortar hydrated and reducing shrinkage during curing. This property enhances the durability of the insulation system and prolongs its lifespan.
Compatibility with Various Insulation Materials:
Another advantage of HPMC is its compatibility with a wide range of insulation materials commonly used in exterior wall systems, including expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), mineral wool, and fiberglass. HPMC-based mortars provide excellent adhesion and compatibility with these materials, ensuring a strong and durable insulation layer.
Fire Resistance and Safety:
HPMC offers significant fire resistance properties when used in exterior wall insulation systems. It acts as a protective barrier, retarding the spread of flames and reducing the risk of fire propagation. Additionally, HPMC is non-toxic and environmentally friendly, making it a safe choice for construction applications.
Conclusion:
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and efficiency of exterior wall insulation systems. Its thermal insulation properties, adhesive capabilities, crack resistance, and compatibility with different insulation materials make it an ideal choice for such applications. By incorporating HPMC into exterior wall insulation systems, we can achieve improved energy efficiency, increased durability, and enhanced fire safety in buildings.



.jpg.webp)

