Is the less water used for plastering mortar, the better?
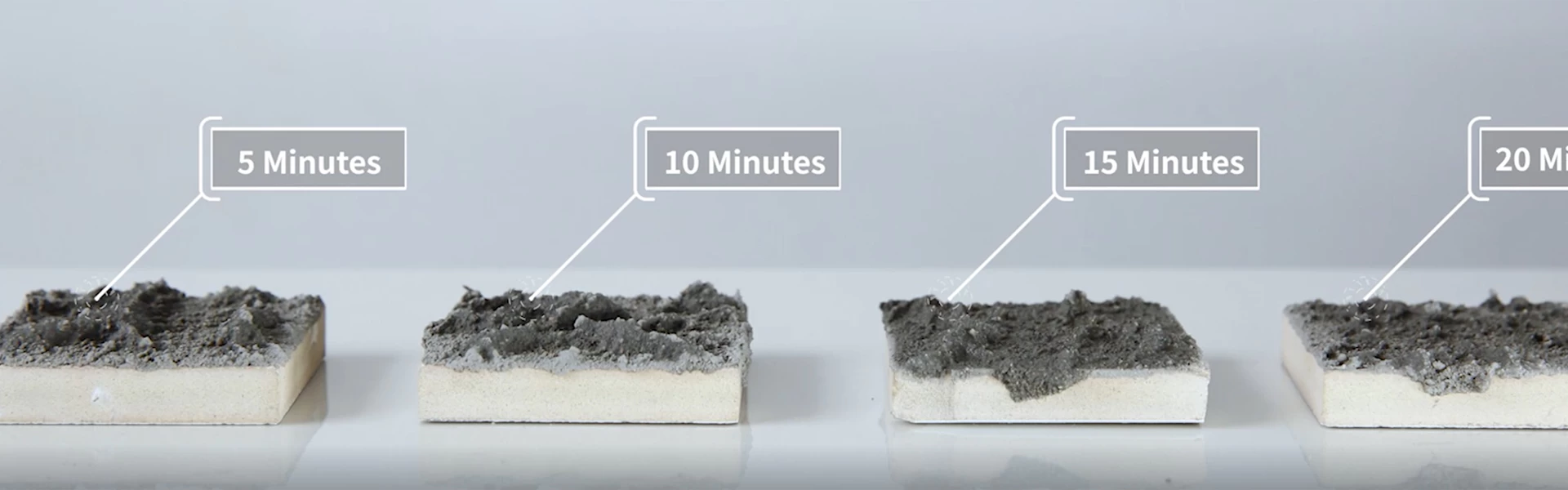
There are many factors affecting the water demand of plastering mortar, which mainly depend on the raw materials, including cementitious materials and fine aggregates. Among them, the amount of aggregate is the largest, so the quality of its material can most affect the water demand of the mortar. For river sand, the reasonable range of water demand for dry-mixed mortar is generally 13-16% (the water demand here refers to the ratio of water to dry material), while the reasonable range of water demand for machine-made sand mortar is generally 13-15%, which exceeds At the maximum water demand, the water retention rate of the mortar will decrease, the bulk density will increase, the workability will become poor, and the strength will be reduced. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the water demand of the mortar. The mortar plant can be carried out by adding water-reducing additives. adjust.

However, when the water demand is less than a specific range, the construction performance of the mortar will also deteriorate, mainly in the lack of fullness of the slurry, and the mortar is not easy to receive. For machine-made sand, the mortar may become sticky and affect the workability. For mortar admixtures with water-reducing effect, when the water-reducing efficiency exceeds a certain limit, the fluidity of the mortar will also increase, which may cause the mortar to sag after being applied to the wall. To sum up, the water requirement of dry-mix plastering mortar varies according to the material, and its reasonable range is different. Too much or too little water will not be conducive to achieving the best state of the mortar. Therefore, it is necessary to master the water requirement of the mortar in a reasonable range.



.jpg.webp)

